二叉搜索树
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)
所谓二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),又叫二叉排序树, 简单而言就是左子树上所有节点的值均小于根节点的值, 而右子树上所有结点的值均大于根节点的值, 左小右大,并不是乱序,因此得名二叉排序树。
一个新事物不能凭空产生,那二叉搜索树又有什么用呢?
有了二叉搜索树,当你要查找一个值, 就不需要遍历整个序列或者说遍历整棵树了, 可以根据当前遍历到的结点的值来确定搜索方向, 这就好比你要去日本,假设你没有见过世界地图, 你不知道该往哪个方向走, 只能满地球找一遍才能保证一定能够到达日本; 而如果你见过世界地图,你知道日本在中国的东边, 你就不会往西走、往南走、往北走。 这种思维在搜索中被叫做“剪枝”, 把不必要的分枝剪掉可以提高搜索效率。 在二叉搜索树中查找值,每次都会把搜索范围缩小, 与二分搜索的思维类似。

创建二叉搜索树
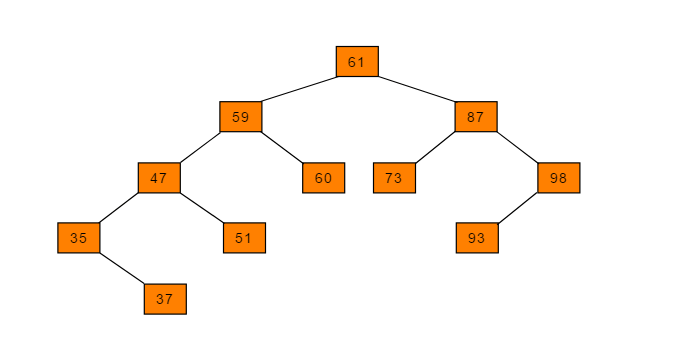
现有序列:A = {61, 87, 59, 47, 35, 73, 51, 98, 37, 93}。根据此序列构造二叉搜索树过程如下:
- i = 0,A[0] = 61,节点61作为根节点;
- i = 1,A[1] = 87,87 > 61,且节点61右孩子为空,故81为61节点的右孩子;
- i = 2,A[2] = 59,59 < 61,且节点61左孩子为空,故59为61节点的左孩子;
- i = 3,A[3] = 47,47 < 59,且节点59左孩子为空,故47为59节点的左孩子;
- i = 4,A[4] = 35,35 < 47,且节点47左孩子为空,故35为47节点的左孩子;
- i = 5,A[5] = 73,73 < 87,且节点87左孩子为空,故73为87节点的左孩子;
- i = 6,A[6] = 51,47 < 51,且节点47右孩子为空,故51为47节点的右孩子;
- i = 7,A[7] = 98,98 < 87,且节点87右孩子为空,故98为87节点的右孩子;
- i = 8,A[8] = 93,93 < 98,且节点98左孩子为空,故93为98节点的左孩子;
创建完毕后如下图中的二叉搜索树:
构造复杂度
二叉搜索树的构造过程,也就是将节点不断插入到树中适当位置的过程。该操作过程,与查询节点元素的操作基本相同,不同之处在于:
- 查询节点过程是,比较元素值是否相等,相等则返回,不相等则判断大小情况,迭代查询左、右子树,直到找到相等的元素,或子节点为空,返回节点不存在
- 插入节点的过程是,比较元素值是否相等,相等则返回,表示已存在,不相等则判断大小情况,迭代查询左、右子树,直到找到相等的元素,或子节点为空,则将节点插入该空节点位置。
由此可知,单个节点的构造复杂度和查询复杂度相同,为 ~。
使用二叉搜索树可以提高查找效率,其平均时间复杂度为O(log2n)。
二叉搜索树的两种极端情况:
- 完全二叉树,所有节点尽量填满树的每一层,上一层填满后还有剩余节点的话,则由左向右尽量填满下一层
- 每一层只有一个节点的二叉树。如下图所示:

插入
插入流程:
- 先检测该元素是否在树中已经存在。如果已经存在,则不进行插入;
- 若元素不存在,则进行查找过程,并将元素插入在查找结束的位置。
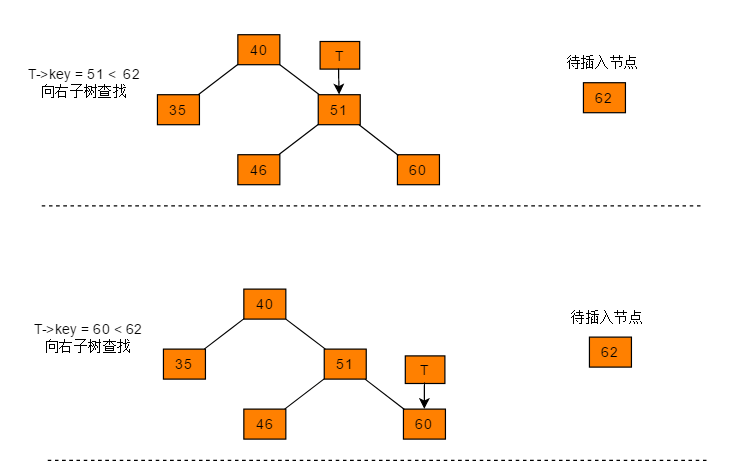
图解过程


删除复杂度
二叉搜索树的节点删除包括两个过程,查找和删除。查询的过程和查询复杂度已知, 这里说明一下删除节点的过程。
节点的删除有以下三种情况:
- 待删除节点度为零;
- 待删除节点度为一;
- 待删除节点度为二。
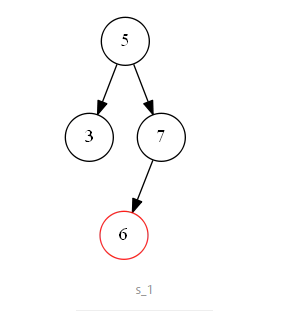
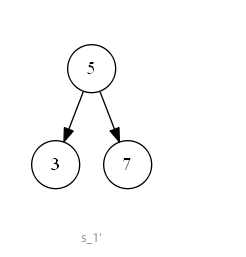
第一种情况如下图 s_1 所示,待删除节点值为 “6”, 该节点无子树,删除后并不影响二叉搜索树的结构特性, 可以直接删除。即二叉搜索树中待删除节点度为零时, 该节点为叶子节点,可以直接删除;
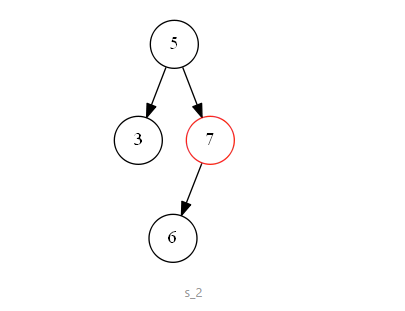
第二种情况如下图 s_2 所示,待删除节点值为 “7”,该节点有一个左子树,删除节点后,为了维持二叉搜索树结构特性,需要将左子树“上移”到删除的节点位置上。即二叉搜索树中待删除的节点度为一时,可以将待删除节点的左子树或右子树“上移”到删除节点位置上,以此来满足二叉搜索树的结构特性。

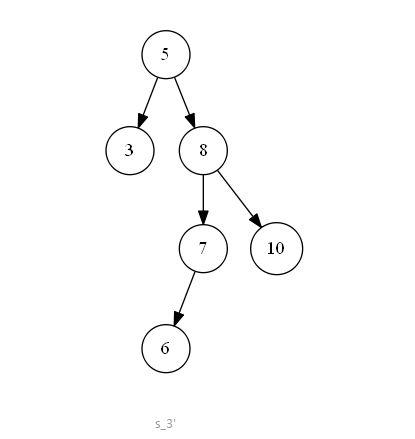
第三种情况如下图 s_3 所示,待删除节点值为 “9”,该节点既有左子树,也有右子树,删除节点后,为了维持二叉搜索树的结构特性,需要从其左子树中选出一个最大值的节点,“上移”到删除的节点位置上。即二叉搜索树中待删除节点的度为二时,可以将待删除节点的左子树中的最大值节点“移动”到删除节点位置上,以此来满足二叉搜索树的结构特性。
其实在真实的实现代码中,该情况下的实际节点删除操作是:
1.查找出左子树中的最大值节点
2.替换待删除节点 的值为 的值
3.删除 节点
因为 作为左子树的最大值节点,所以节点的度一定是 0 或 1,所以删除节点的情况就转移为以上两种情况。

之前提到二叉搜索树中节点的删除操作,包括查询和删除两个过程,这里称删除节点后,维持二叉搜索树结构特性的操作为“稳定结构”操作,观察以上三种情况可知:
- 前两种情况下,删除节点后,“稳定结构”操作的复杂度都是常数级别,即整个的节点删除操作复杂度为 ~;
- 第三种情况下,设删除的节点为 ,“稳定结构”操作需要查找 节点左子树中的最大值,也就是左子树中最“右”的叶子结点,即“稳定结构”操作其实也是一种内部的查询操作,所以整个的节点删除操作其实就是两个层次的查询操作,复杂度同为 ~;
性能分析
由以上查询复杂度、构造复杂度和删除复杂度的分析可知,三种操作的时间复杂度皆为 ~。下面分析线性结构的三种操作复杂度,以二分法为例:
- 查询复杂度,时间复杂度为 ,优于二叉搜索树;
- 元素的插入操作包括两个步骤,查询和插入。查询的复杂度已知,插入后调整元素位置的复杂度为 ,即单个元素的构造复杂度为:
- 删除操作也包括两个步骤,查询和删除,查询的复杂度已知,删除后调整元素位置的复杂度为 ,即单个元素的删除复杂度为: 由此可知,二叉搜索树相对于线性结构,在构造复杂度和删除复杂度方面占优;在查询复杂度方面,二叉搜索树可能存在类似于斜树,每层上只有一个节点的情况,该情况下查询复杂度不占优势。
总结
二叉搜索树的节点查询、构造和删除性能,与树的高度相关,如果二叉搜索树能够更“平衡”一些,避免了树结构向线性结构的倾斜,则能够显著降低时间复杂度。二叉搜索树的存储方面,相对于线性结构只需要保存元素值,树中节点需要额外的空间保存节点之间的父子关系,所以在存储消耗上要高于线性结构。
package datastructure.tree;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
/**
* 二叉排序树:二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),又称二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),也称二叉搜索树。
*
* @author liuyi27
*
* <p>
* 二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
* </p>
* <p>
* (1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于或等于它的根结点的值;
* </p>
* <p>
* (2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于或等于它的根结点的值;
* </p>
* <p>
* (3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
* </p>
*
*/
@Setter
public class BinarySortTree {
private int data;
private BinarySortTree lchild, rchild;
/**
* 递归查找二叉排序树T中是否存在key 指针f指向T的双亲,其初始调用值为NULL 若查找成功,* 则指针p指向该数据元素结点,并返回TRUE
* 否则指针p指向查找路径上访问的最后一个结点并返回FALSE
*/
// 如果树是空的,则查找结束,无匹配。
// 如果被查找的值和根结点的值相等,查找成功。否则就在子树中继续查找。如果被查找的值小于根结点的值就选择左子树,大于根结点的值就选择右子树。
public static boolean search(BinarySortTree tree, int key) {
if (tree == null) {
return false;
}
if (tree.data == key) {
return true;
}
System.out.println(tree.data);
if (key < tree.data) {
System.out.println("<");
/* 在左子树中继续查找 */
return search(tree.lchild, key);
} else {
System.out.println(">");
/* 在右子树中继续查找 */
return search(tree.rchild, key);
}
}
/**
* 若查找的key已经有在树中,则p指向该数据结点。 若查找的key没有在树中,则p指向查找路径上最后一个结点。
*
* @param tree
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static BinarySortTree add(BinarySortTree tree, int key) {
if (tree == null) {
tree = new BinarySortTree();
tree.data = key;
return tree;
}
if (key < tree.data) {
tree.lchild = add(tree.lchild, key);
} else {
tree.rchild = add(tree.rchild, key);
}
return tree;
}
public static BinarySortTree create(BinarySortTree tree, int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
tree = add(tree, array[i]);
}
return tree;
}
public static boolean remove(BinarySortTree tree, int key) {
if (tree == null) {
return false;
}
if (tree.data == key) {
return delete(tree);
} else if (tree.data > key) {
return remove(tree.lchild, key);
} else {
return remove(tree.rchild, key);
}
}
/**
* 1)删除结点为叶子结点; 2)删除的结点只有左子树; 3)删除的结点只有右子树 4)删除的结点既有左子树又有右子树。
*
* @param tree
* @return
*/
private static boolean delete(BinarySortTree tree) {
if (tree.rchild == null) {
// 右子树空则只需重接它的左子树(待删结点是叶子也走此分支)
tree = tree.lchild;
} else if (tree.lchild == null) {
// 只需重接它的右子树
tree = tree.rchild;
} else {
// 左右子树均不空
// 转左
BinarySortTree tempP = null;
BinarySortTree temp = tree.lchild;
// 然后向右到尽头(找待删结点的前驱)
while (temp.rchild != null) {
tempP = temp;
temp = temp.rchild;
}
// TODO 感觉非常有问题
if (tempP != null) {
tempP.rchild = null;
}else {
temp.lchild = null;
}
// 将被删结点前驱的值取代被删结点的值(指向被删结点的直接前驱)
tree.data = temp.data;
}
return true;
}
public static void layerOrder(BinarySortTree node, Queue<BinarySortTree> queue) {
if (node != null && queue.isEmpty()) {
// 将当前节点放入队列首指针所指位置
queue.add(node);
System.out.print(queue.poll().data + " ");
} else {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
if (node.lchild != null) {
queue.add(node.lchild);
}
if (node.rchild != null) {
queue.add(node.rchild);
}
BinarySortTree nextNode = queue.poll();
if (nextNode != null) {
layerOrder(nextNode, queue);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 10, 4, 6, 34, 32, 5, 2, 1, 11, 23 };
BinarySortTree tree = null;
tree = create(tree, array);
Queue<BinarySortTree> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<BinarySortTree>();
layerOrder(tree, queue);
System.out.println("查找1");
// System.out.println(search(tree, 10));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 4));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 6));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 34));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 32));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 5));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 2));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 11));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 23));
System.out.println("查找1");
boolean result = remove(tree, 4);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(result);
layerOrder(tree, queue);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("查找2");
// System.out.println(search(tree, 10));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 4));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 34));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 32));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 2));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 11));
// System.out.println(search(tree, 23));
System.out.println(search(tree, 5));
System.out.println(search(tree, 6));
}
}
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 二叉搜索树
* @author 爱学习的程序员
* @version V1.0
*/
public class BST{
// 根结点
public static Node root = null;
/**
* 二叉搜索树的结点类
*/
public static class Node{
// 父结点
Node p;
// 左孩子
Node left;
// 右孩子
Node right;
// 关键字
int key;
public Node(Node p, Node left, Node right, int key){
this.p = p;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.key = key;
}
}
/**
* 插入结点
* @param z 待插入结点
* @return 根结点
*/
public static void insert(Node z){
// 树为空,直接作为根结点
if(root == null)
root = z;
else{
Node y = null;
Node x = root;
// 寻求树中结点z的合适位置
while(x != null){
y = x;
if(z.key < x.key)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
z.p = y;
if(z.key < y.key)
y.left = z;
else
y.right = z;
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历二叉搜索树
* @param x 树中结点
* @return 无
*/
public static void inorderTreeWalk(Node x){
if(x!=null){
inorderTreeWalk(x.left);
System.out.print(x.key+"\t");
inorderTreeWalk(x.right);
}
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树中查找一个具有指定关键字的结点
* @param x 树中结点
* @param k 关键字
* @return 无
*/
public static Node search(Node x, int k){
while(x != null && x.key != k){
if(k < x.key)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
return x;
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树中关键字最小的结点
* @param x 树中结点
* @return 关键字最小的结点
*/
public static Node minimum(Node x){
while(x.left != null)
x = x.left;
return x;
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树中关键字最大的结点
* @param x 树中结点
* @return 关键字最大的结点
*/
public static Node maxmum(Node x){
while(x.right != null)
x = x.right;
return x;
}
/**
* 结点的后继(中序遍历)
* @param x 树中结点
* @return 结点的后继
*/
public static Node successor(Node x){
// 如果x的右子树不为空,则x的后继为x的右子树中具有最小关键字的结点
if(x.right != null)
return minimum(x.right);
// 如果x的右子树为空,则x的后继为x的最底层祖先,而且它的左孩子也是x的一个祖先(左孩子是x即可)
else{
Node y = x.p;
while(y !=null && x == y.right){
x = y;
y = y.p;
}
return y;
}
}
/**
* 结点的先驱(代码与结点的后继对称)
* @param x 树中结点
* @return 结点的先驱
*/
public static Node predecessor(Node x){
if(x.left != null)
return maxmum(x.left);
else{
Node y = x.p;
while(y !=null && x == y.left){
x = y;
y = y.p;
}
return y;
}
}
/**
* 二叉搜索树内移动子树(用另一棵子树替换一棵子树,并成为其父结点的孩子结点)
* @param u 被替换子树的根结点
* @param v 替换子树的根结点
* @return 无
*/
public static void transplant(Node u, Node v){
if(u.p == null)
root = v;
else if(u == u.p.left)
u.p.left = v;
else
u.p.right = v;
if(v != null)
v.p = u.p;
}
/**
* 删除指定结点
* @param z 待删除结点
* @return 无
*/
public static void delete(Node z){
// 如果z最多有一个孩子结点,则直接调用transplant
if(z.left == null)
transplant(z, z.right);
else if(z.right == null)
transplant(z, z.left);
// 如果z两个孩子结点都存在,则寻找其后继
else{
// z的后继
Node y = minimum(z.right);
if(y.p != z){
transplant(z, z.right);
y.right = z.right;
y.right.p = y;
}
transplant(z, y);
y.left = z.left;
y.left.p = y;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Random rand = new Random();
// 结点数组
Node[] node = new Node[10];
int i = 0;
System.out.println("生成二叉树结点并插入树中:");
for(i = 0; i < node.length ;i++){
node[i] = new Node(null, null, null, rand.nextInt(100) + 1);
System.out.print(node[i].key+"\t");
insert(node[i]);
}
// 中序遍历
System.out.println("\n"+"中序遍历二叉搜索树:");
inorderTreeWalk(root);
// 查找指定结点
Node x = search(root, node[5].key);
System.out.println("\n"+"查找结果:");
System.out.println("自身关键字:"+x.key+"\t"+"父结点的关键字:"+x.p.key);
// 具有最小关键字的结点
x = minimum(root);
System.out.println("树中最小关键字:"+x.key);
// 具有最大关键字的结点
x = maxmum(root);
System.out.println("树中最大关键字:"+x.key);
// x的后继
x = predecessor(node[5]);
System.out.println("前驱的关键字:"+x.key);
// x的前驱
x = successor(node[5]);
System.out.println("后继的关键字:"+x.key);
// 删除结点,并中序输出观看结果
delete(node[5]);
System.out.println("删除结点:");
inorderTreeWalk(root);
}
}