ApplicationContext体系结构分析
上篇已经对IoC容器的设计进行了分析,本篇将对ApplicationContext经典的继承层次图进行详细的分析
本节代码基于springboot 2.3.0
继承层次图概览
使用IDEA的继承层次工具生成如下的图(选中ApplicationContext --> Ctrl+H):
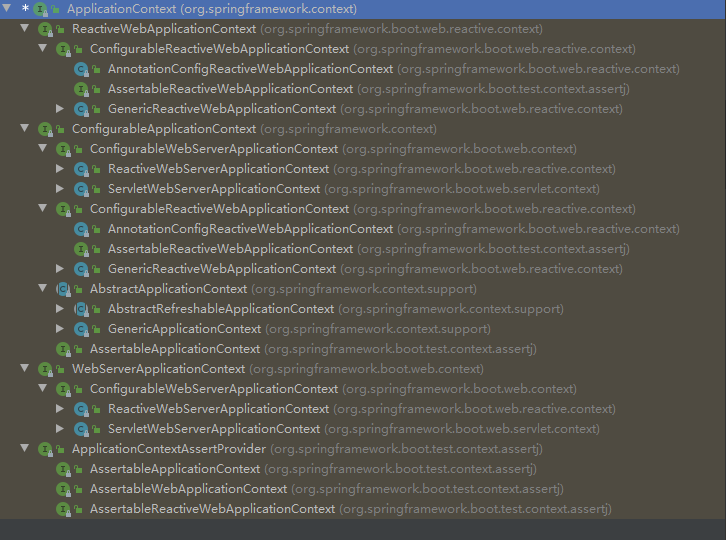
从上图能很清楚的看出,ApplicationContext的子接口分为四个部分:
- ConfigurableApplicationContext:大部分的应用上下文都实现了该接口
- ReactiveWebApplicationContext: 在reactive方案容器的运行web的应用程序中使用
- WebServerApplicationContext:在servlet方案容器运行web的应用程序中使用
- ApplicationContextAssertProvider: 它另外支持AssertJ样式声明。可用于装饰现有的应用程序上下文或启动失败的应用程序上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext分析
从上面的类的继承层次图能看到,ConfigurableApplicationContext是比较上层的一个接口,该接口也是比较重要的一个接口,几乎所有的应用上下文都实现了该接口。 该接口在ApplicationContext的基础上提供了配置应用上下文的能力,此外提供了生命周期的控制能力。先看一下该接口的继承关系图(为了更加简洁,去掉了ApplicationContext继承的接口):
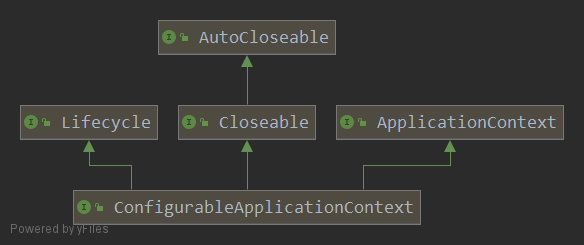
Closeable接口用于关闭应用上下文,释放所有的资源和锁,这也包括摧毁所有缓存的单例的bean,常见的try-with-resources用法如下,执行完try体中的代码后会自动的调用close方法:
try (ConfigurableApplicationContext cac = ...) {
// 编写代码
...
}
Lifecycle定义了启动/停止生命周期的控制的一些方法,其中的方法如下:
void start(); // 启动组件
void stop(); // 停止组件
boolean isRunning(); // 组件是否正在运行
接下来看一下ConfigurableApplicationContext中的方法:
String CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n";
String CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME = "conversionService";
String LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME = "loadTimeWeaver";
String ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "environment";
String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME = "systemProperties";
String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
String SHUTDOWN_HOOK_THREAD_NAME = "SpringContextShutdownHook";
// 设置应用上下文唯一的id
void setId(String id);
// 设置应用程序上下文的父级
void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent);
// 设置应用上下文的环境
void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
@Override
ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();
// 添加一个新的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
void addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor);
// 添加应用程序监听器
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
// 添加协议解析器,可能会覆盖默认的规则
void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver);
// 加载或者刷新配置
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
// 向JVM runtime注册一个关闭钩子,JVM关闭时关闭这个上下文
void registerShutdownHook();
@Override
void close();
// 应用程序上下文是否是激活状态
boolean isActive();
// 获取应用上下文内部的bean factory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
上面的这些方法基本上是提供了对某些特性的实现进行支撑的方法。
看了这么多方法,下面看一下ApplicationContext的抽象的实现。
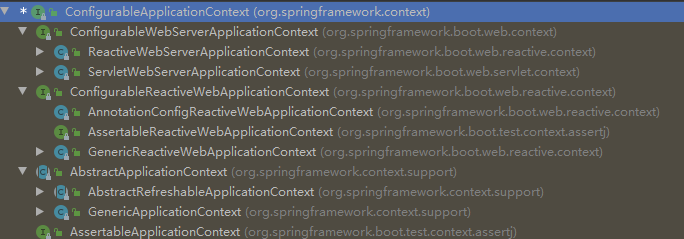
AbstractApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext是ApplicationContext接口的抽象实现,这个抽象类仅仅是实现了公共的上下文特性。 这个抽象类使用了模板方法设计模式,需要具体的实现类去实现这些抽象的方法。对相关接口的实现如下:
- ApplicationContext接口的实现
- ConfigurableApplicationContext接口的实现
- BeanFactory接口的实现
- ListableBeanFactory接口的实现
- HierarchicalBeanFactory接口的实现
- MessageSource接口的实现
- ResourcePatternResolver的实现
- Lifecycle接口的实现
本文不会详细的讲解这个类中的具体的实现细节,后面会有更加的详细的介绍。下面看下里面的抽象方法:
// 刷新BeanFactory,用于执行实际的配置加载,该方法在其他的初始化工作之前被refresh()方法调用
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
// 关闭BeanFactory,用于释放内部使用的BeanFactory·
protected abstract void closeBeanFactory();
// 获取内部使用的BeanFactory
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
那么对需要实现的方法经过抽象后,只剩下少量的需要子类去实现的方法。
GenericApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext继承自AbstractApplicationContext,是为通用目的设计的,它能加载各种配置文件,例如xml,properties等等。 它的内部持有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory的实例,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,以便允许向其应用任何bean的定义的读取器。 为了能够注册bean的定义,refresh()只允许调用一次。常见的使用如下:
GenericApplicationContext ctx = new GenericApplicationContext();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader propReader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(ctx);
propReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("otherBeans.properties"));
ctx.refresh();
MyBean myBean = (MyBean) ctx.getBean("myBean");
..
这个类的实现没有太多需要注意的地方,需要注意的有两点:
- 内部使用的DefaultListableBeanFactory的实例,提供了一些方法来配置该实例,例如是否允许bean定义的覆盖、是否允许bean之间的循环应用等等。
- 该类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry,bean的定义注册。以便能通过BeanDefinitionReader读取bean的配置,并注册。BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的实现是直接使用内部的DefaultListableBeanFactory的实例。
GenericApplicationContext有六个子类
- GenericXmlApplicationContext:内置了对XML的支持。它非常的方便和灵活,是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的一种替代品。可以发现,它的内部有一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader的实例,专门用于处理XML的配置。
- StaticApplicationContext:主要用于编程式的注入bean和消息,而不是从外部的配置源读取bean的定义。主要是在测试时非常有用。通过阅读源代码可以看到,它的内部有一个StaticMessageSource的实例,使用addMessage方法添加消息。每次在编程式的注入bean时,都会创建一个GenericBeanDefinition的实例。
- ResourceAdapterApplicationContext:是为JCA(J2EE Connector Architecture)的ResourceAdapter设计的,主要用于传递BootstrapContext的实例给实现了BootstrapContextAware接口且由spring管理的bean。覆盖了postProcessBeanFactory方法来实现此功能。
- GenericGroovyApplicationContext:实现了GroovyObject接口以便能够使用点的语法(.xx)取代getBean方法来获取bean。它主要用于Groovy bean的定义,与GenericXmlApplicationContext一样,它也能解析XML格式定义的bean。内部使用GroovyBeanDefinitionReader来完成groovy脚本和XML的解析。
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:提供了注解配置(例如:Configuration、Component、inject等)和类路径扫描(scan方法)的支持,可以使用register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses)来注册一个一个的进行注册。实现了AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,来完成对注册配置的支持,只有两个方法:register和scan。内部使用AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader来完成注解配置的解析,使用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来完成类路径下的bean定义的扫描。
- GenericReactiveWebApplicationContext:
WebServerApplicationContext
该接口提供了在web应用中的配置,并提供如下接口
//返回由上下文创建的WebServer;如果尚未创建服务器,则返回null
WebServer getWebServer();
//返回Web服务器应用程序上下文的名称空间;如果未设置名称空间,则返回null。 当多个Web服务器在同一应用程序中运行时(例如,在不同端口上运行的管理上下文),用于消除歧义
String getServerNamespace();
//如果指定的上下文是具有匹配服务器名称空间的WebServerApplicationContext,则返回true。
static boolean hasServerNamespace(ApplicationContext context, String serverNamespace) {
return (context instanceof WebServerApplicationContext) && ObjectUtils
.nullSafeEquals(((WebServerApplicationContext) context).getServerNamespace(), serverNamespace);
}
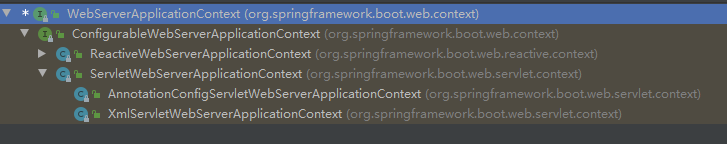
ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext继承自WebApplicationContext和ConfigurableApplicationContext,并额外添加一个接口
void setServerNamespace(String serverNamespace);
ServletWebServerApplicationContext
ServletWebServerApplicationContext继承了GenericWebApplicationContext并实现了ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext
ApplicationContext容器的设计原理
以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为例应用:
// 根据配置文件创建spring容器
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 从容器中获取Bean
ConferenceServiceImpl conferenceService = (ConferenceServiceImpl)context.getBean("conferenceService");
// 调用Bean方法
conferenceService.conference();
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext源码:
package org.springframework.context.support;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext {
private Resource[] configResources;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, refresh, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path, Class<?> clazz) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {path}, clazz);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] paths, Class<?> clazz) throws BeansException {
this(paths, clazz, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] paths, Class<?> clazz, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
Assert.notNull(paths, "Path array must not be null");
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class argument must not be null");
this.configResources = new Resource[paths.length];
for (int i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
this.configResources[i] = new ClassPathResource(paths[i], clazz);
}
refresh();
}
@Override
protected Resource[] getConfigResources() {
return this.configResources;
}
}
构造器传入XML最后会调用到如下构造器:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
最后会调用refresh()方法,这个方法就是IOC容器启动的入口,IOC容器里面进行了一序列复杂的操作,
这也是通往IOC容器核心实现原理的入口。