SpringBoot中如何启动Tomcat流程
本章代码基于springboot 2.2.2
SpringBoot项目之所以部署简单,其很大一部分原因就是因为不用自己折腾Tomcat相关配置,因为其本身内置了各种Servlet容器。 一直好奇: SpringBoot是怎么通过简单运行一个main函数,就能将容器启动起来,并将自身部署到其上 。此文想梳理清楚这个问题。
我们从SpringBoot的启动入口中分析:
Context 创建
// Create, load, refresh and run the ApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
在SpringBoot 的 run 方法中,我们发现其中很重要的一步就是上面的一行代码。注释也写的很清楚:
创建、加载、刷新、运行 ApplicationContext。
继续往里面走。
/**
* Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this
* method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context
* class before falling back to a suitable default.
* @return the application context (not yet refreshed)
* @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class)
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
逻辑很清楚:
先找到 context 类,然后利用工具方法将其实例化。
如果是 web 环境,则加载DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS类。参看成员变量定义,其类名为:
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
此类的继承结构如图:
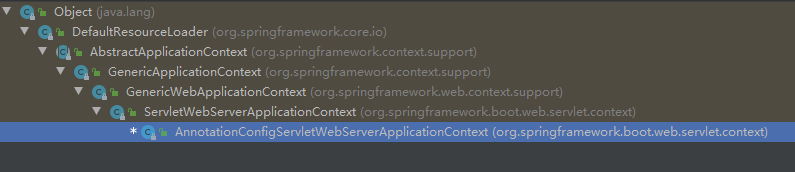
直接继承GenericWebApplicationContext。关于该类前文已有介绍,只要记得它是专门为 web application提供context 的就好。
refresh
在经历过 Context 的创建以及Context的一系列初始化之后,调用 Context 的 refresh 方法,真正的好戏才开始上演。
SpringApplication
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
可以看到refresh直接调用的试 AbstractApplicationContext 的refresh()方法
而且查看 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 本身没有实现refresh(), 找到其直接父类:ServletWebServerApplicationContext也是调用上级方法到 AbstractApplicationContext。
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
stopAndReleaseWebServer();
throw ex;
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
看11行 onRefresh();, AbstractApplicationContext本身onRefresh()没有实现任何东西;最后我们回归到它的实现类。 根据上面的类结构图我们找到 ServletWebServerApplicationContext
ServletWebServerApplicationContext
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
我们重点看第3行。代码第3行createWebServer根据名字是要创建一个web服务,
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
根据逻辑和进入getServletContext()可知,这里webServer和servletContext应该都是null或者servletContext不为null
- 先看都是null的情况
获取到了一个ServletWebServerFactory,这是一个接口我们可以找到5个实现。不用想当然是要看TomcatServletWebServerFactory
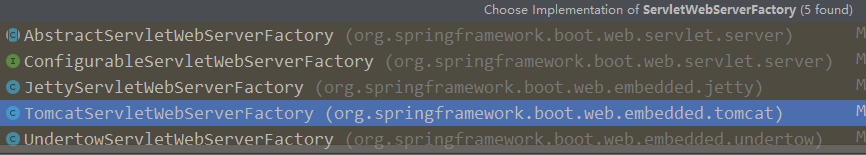
TomcatServletWebServerFactory
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
哈哈哈!看见Tomcat了。
从第7行 Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol) 一直到第16行完成了tomcat的connector的添加。 tomcat中的connector主要负责用来处理http请求,具体原理可以参看Tomcat的源码,此处暂且不提。
prepareContext方法有点长,重点看其中的几行:
if (isRegisterDefaultServlet()) {
addDefaultServlet(context);
}
if (shouldRegisterJspServlet()) {
addJspServlet(context);
addJasperInitializer(context);
}
context.addLifecycleListener(new StaticResourceConfigurer(context));
ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers);
host.addChild(context);
configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
前面两个分支判断添加了默认的servlet类和与jsp 相关的 servlet 类。
对所有的ServletContextInitializer进行合并后,利用合并后的初始化类对context 进行配置。
返回TomcatServletWebServerFactory,顺着getTomcatWebServer方法一直往下走,开始正式启动Tomcat。
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
this.tomcat.start();正式启动 tomcat。
现在我们回过来看看之前的那个 getSelfInitializer()方法:
是这里的 this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
/**
* Returns the {@link ServletContextInitializer} that will be used to complete the
* setup of this {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* @return the self initializer
* @see #prepareWebApplicationContext(ServletContext)
*/
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return this::selfInitialize;
}
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
prepareWebApplicationContext方法中主要是将ServletContext设置为rootContext。
registerApplicationScope允许用户存储自定义的scope。并且将web专用的scope注册到BeanFactory中,比如("request", "session", "globalSession", "application")。
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans 注册web专用的environment bean(比如 ("contextParameters", "contextAttributes"))到给定的 BeanFactory 中。
beans.onStartup(servletContext)比较重要,主要用来配置 servlet、filters、listeners、context-param和一些初始化时的必要属性。
以其一个实现类ServletContextInitializer试举一例:
@Override
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
register(description, servletContext);
}